Font Utilities¶
dartwork-mpl provides helper functions and automatic font registration to simplify typography management in your visualizations.
Automatic Font Registration¶
When you import dartwork-mpl, all bundled fonts are automatically registered with matplotlib’s font manager:
import dartwork_mpl as dm # Fonts are now available!
This happens through the _add_fonts() function in the font module:
from pathlib import Path
from matplotlib import font_manager
def _add_fonts():
font_dir = [Path(__file__).parent / 'asset/font']
for font in font_manager.findSystemFonts(font_dir):
font_manager.fontManager.addfont(font)
_add_fonts() # Called on import
No manual installation or system-level font configuration required.
fs(n) - Font Size Helper¶
Adjusts font size relative to the current base size from rcParams.
Signature:
dm.fs(n)
Parameters:
n(int/float): Points to add to the base font size
Returns:
float: The adjusted font size
How It Works:
def fs(n):
return plt.rcParams['font.size'] + n
Example:
import dartwork_mpl as dm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dm.style.use("scientific") # Base font size is 8.5
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_title("Main Title", fontsize=dm.fs(6)) # 14.5pt
ax.set_xlabel("X Label", fontsize=dm.fs(2)) # 10.5pt
ax.set_ylabel("Y Label", fontsize=dm.fs(0)) # 8.5pt (base)
ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "Note", fontsize=dm.fs(-2)) # 6.5pt
Why Use fs()?
Using relative sizes keeps your typography consistent when switching between styles or output formats:
# Instead of hardcoding:
ax.set_title("Title", fontsize=14) # May not fit your style
# Use relative sizing:
ax.set_title("Title", fontsize=dm.fs(4)) # Always 4pt larger than base
fw(n) - Font Weight Helper¶
Adjusts font weight relative to the current base weight from rcParams.
Signature:
dm.fw(n)
Parameters:
n(int): Weight steps to add (each step = 100)
Returns:
int: The adjusted font weight
How It Works:
def fw(n):
return plt.rcParams['font.weight'] + 100 * n
Example:
import dartwork_mpl as dm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dm.style.use("scientific") # Base weight is 300 (Light)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_title("Bold Title", fontweight=dm.fw(4)) # 700 (Bold)
ax.set_xlabel("Medium Label", fontweight=dm.fw(2)) # 500 (Medium)
ax.set_ylabel("Light Label", fontweight=dm.fw(0)) # 300 (Light, base)
ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "Thin", fontweight=dm.fw(-2)) # 100 (Thin)
Weight Scale Reference:
|
Result |
Weight Name |
|---|---|---|
|
100 |
Thin |
|
200 |
ExtraLight |
|
300 |
Light (base) |
|
400 |
Regular |
|
500 |
Medium |
|
600 |
SemiBold |
|
700 |
Bold |
|
800 |
ExtraBold |
|
900 |
Black |
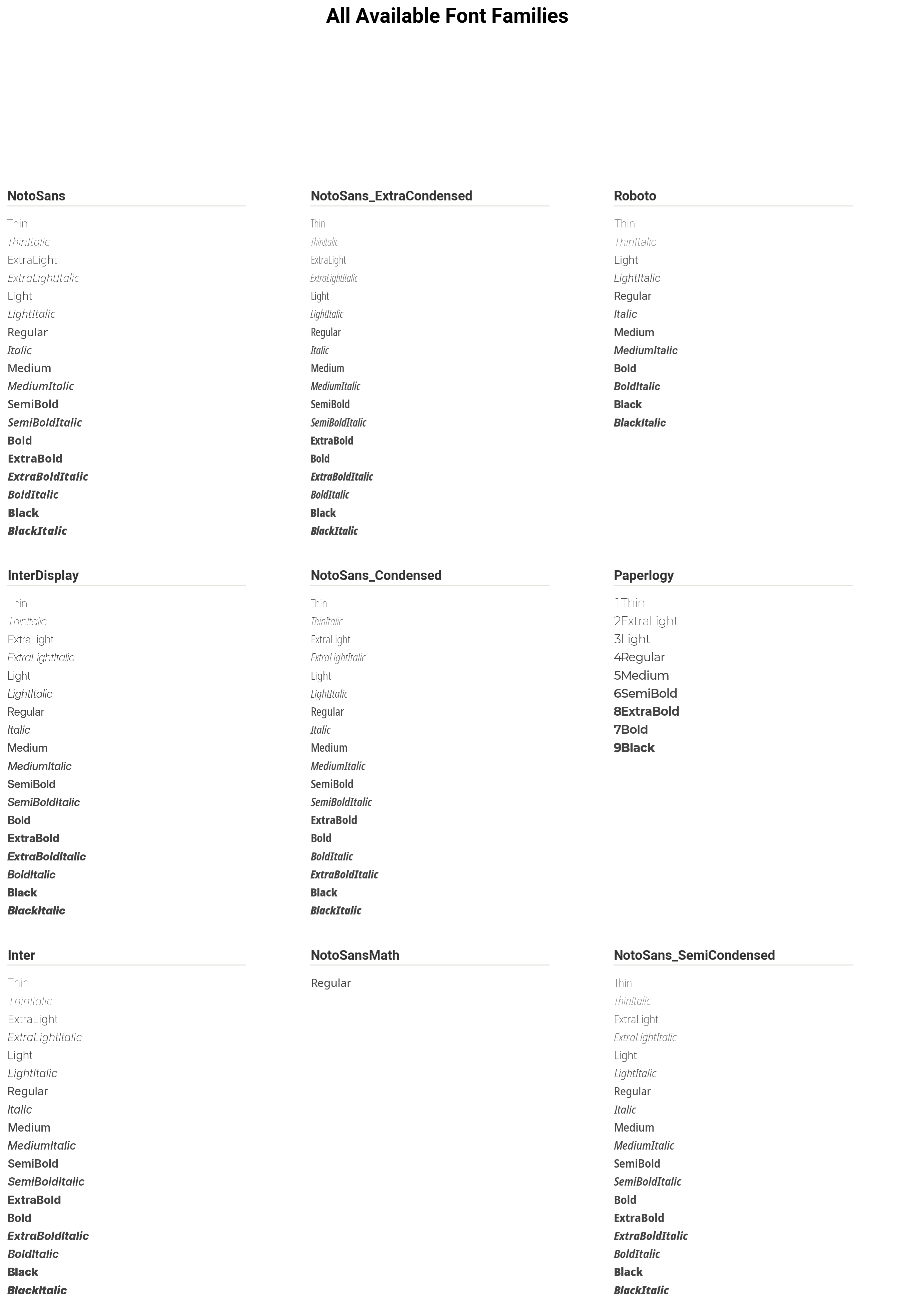
plot_fonts() - Font Preview Gallery¶
Generates a visual preview of all available fonts.
Signature:
dm.plot_fonts(font_dir=None, ncols=3, font_size=11)
Parameters:
font_dir(str, optional): Directory containing.ttffiles. Defaults to the bundled fonts.ncols(int): Number of columns in the preview grid. Default: 3font_size(int): Sample text size in points. Default: 11
Returns:
matplotlib.figure.Figure: The preview figure
Example:
import dartwork_mpl as dm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Preview bundled fonts
fig = dm.plot_fonts(ncols=3, font_size=12)
plt.show()
# Preview custom fonts
fig = dm.plot_fonts(font_dir="/path/to/custom/fonts", ncols=2)
plt.savefig("custom_fonts.png", dpi=150)
Style Configuration¶
dartwork-mpl styles configure fonts through matplotlib’s rcParams:
Default Font Settings (dmpl style)¶
# Font family and weight
font.family: roboto
font.weight: 300
# Base font size
font.size: 8.5
# Math text configuration
mathtext.fontset: custom
mathtext.rm: Noto Sans Math
mathtext.it: Noto Sans Math:italic
mathtext.bf: Noto Sans Math:bold
mathtext.cal: Noto Sans Math
mathtext.sf: Noto Sans Math
mathtext.tt: Noto Sans Math
Applying Styles¶
import dartwork_mpl as dm
# Apply a preset (recommended)
dm.style.use("scientific")
dm.style.use("presentation")
Custom Font Configuration¶
Override defaults for specific needs:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import dartwork_mpl as dm
dm.style.use("scientific")
# Change font family
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'Inter'
# Change base weight
plt.rcParams['font.weight'] = 400 # Regular instead of Light
# Change base size
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 10
Tips and Best Practices¶
Consistent Typography Hierarchy¶
Use fs() to create a consistent sizing hierarchy:
# Define your hierarchy
TITLE_SIZE = dm.fs(6)
SUBTITLE_SIZE = dm.fs(3)
LABEL_SIZE = dm.fs(0)
ANNOTATION_SIZE = dm.fs(-2)
# Apply consistently
ax.set_title("Main Title", fontsize=TITLE_SIZE)
ax.text(0.5, 0.95, "Subtitle", fontsize=SUBTITLE_SIZE, transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.set_xlabel("X Axis", fontsize=LABEL_SIZE)
Emphasis with Weight¶
Use weight for emphasis instead of color when possible:
ax.set_title("Important Finding", fontweight=dm.fw(4)) # Bold
ax.set_xlabel("Supporting Label", fontweight=dm.fw(0)) # Light
Condensed Fonts for Tight Spaces¶
Switch to condensed variants when space is limited:
# For crowded tick labels
ax.tick_params(axis='x', labelsize=dm.fs(-1))
for label in ax.get_xticklabels():
label.set_fontfamily('Noto Sans Condensed')
Math Text¶
Use raw strings with LaTeX-style notation:
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\alpha$ (radians)')
ax.set_ylabel(r'$\sin(\alpha)$')
ax.set_title(r'$y = \sum_{i=1}^{n} x_i$')