Color Space¶
dartwork-mpl provides a powerful Color class for working with colors in different
color spaces, with a focus on OKLab and OKLCH for perceptually uniform color
operations. This page covers creating Color objects, converting between color
spaces, modifying color components, copying colors, interpolating colors, and
generating custom colormaps.
Color object¶
The Color class is a unified interface for working with colors across multiple
color spaces. Internally, colors are stored as OKLab coordinates, which enables
efficient and accurate conversions between different color representations.
import dartwork_mpl as dm
# All Color objects are stored internally as OKLab
color = dm.oklab(0.7, 0.1, 0.2)
print(color) # Color(oklab=(0.7000, 0.1000, 0.2000))
View objects: Color objects provide view properties (oklab, oklch, rgb)
for convenient attribute-based access to color components. These views support
reading, writing, unpacking, and indexing operations, making it easy to work
with individual color channels.
Creating Color objects¶
You can create Color objects from any supported color space using convenient wrapper functions or class methods.
From OKLab coordinates¶
import dartwork_mpl as dm
# L: lightness (0-1), a, b: color-opponent dimensions
color = dm.oklab(0.7, 0.1, 0.2)
From OKLCH coordinates¶
import dartwork_mpl as dm
# L: lightness (0-1), C: chroma (>=0), h: hue in degrees (0-360)
color = dm.oklch(0.7, 0.2, 120) # Greenish color
OKLCH uses degrees for hue, making it intuitive to work with (0° = red, 120° = green, 240° = blue).
From RGB values¶
import dartwork_mpl as dm
# Automatically detects range: 0-1 or 0-255
color1 = dm.rgb(0.8, 0.2, 0.3) # 0-1 range
color2 = dm.rgb(200, 50, 75) # 0-255 range (auto-detected)
The rgb() function automatically detects whether values are in the 0-1 or 0-255 range.
From hex strings¶
import dartwork_mpl as dm
color1 = dm.hex("#ff5733")
color2 = dm.hex("#f73") # Short format also supported
From matplotlib color names¶
import dartwork_mpl as dm
# Works with any matplotlib color name
color1 = dm.named("red")
color2 = dm.named("oc.blue5") # dartwork-mpl colors
color3 = dm.named("tw.blue500") # Tailwind colors

Creating Color objects. Various ways to initialize Color objects from different color representations. All methods produce equivalent Color instances that can be converted to any supported color space.¶
Color space conversion¶
Once you have a Color object, you can convert it to any supported color space using conversion methods or view objects for convenient access.
Using conversion methods¶
import dartwork_mpl as dm
color = dm.hex("#ff5733")
# Convert to different color spaces (returns tuples)
L, a, b = color.to_oklab() # OKLab coordinates
L, C, h = color.to_oklch() # OKLCH (h in degrees)
r, g, b = color.to_rgb() # RGB (0-1 range)
hex_str = color.to_hex() # Hex string
Using view objects (recommended)¶
View objects provide intuitive attribute-based access to color space components, supporting both reading and writing operations:
import dartwork_mpl as dm
color = dm.hex("#ff5733")
# Attribute-based access
L = color.oklab.L
a = color.oklab.a
b = color.oklab.b
# Unpacking (same as tuple unpacking)
L, a, b = color.oklab
L, C, h = color.oklch
r, g, b = color.rgb
# Index access (alternative to attribute access)
a = color.oklab[1] # Same as color.oklab.a
C = color.oklch[1] # Same as color.oklch.C
g = color.rgb[1] # Same as color.rgb.g
Modifying color components¶
View objects support direct modification of color components using assignment and arithmetic operations:
import dartwork_mpl as dm
color = dm.oklab(0.7, 0.1, 0.2)
# Direct assignment
color.oklab.L = 0.8
color.oklab.a = 0.2
# Arithmetic operations
color.oklab.L += 0.1 # Increase lightness
color.oklab.a -= 0.05 # Decrease green-red component
color.oklab.b *= 1.5 # Multiply blue-yellow component
color.oklab.L /= 2.0 # Divide lightness
# OKLCH modifications
color.oklch.C += 0.1 # Increase chroma (saturation)
color.oklch.h += 30 # Rotate hue by 30 degrees
color.oklch.C *= 1.2 # Multiply chroma
# RGB modifications
color.rgb.r = 0.9 # Set red component
color.rgb.g += 0.1 # Increase green component
color.rgb.b *= 1.5 # Multiply blue component
Note: When modifying OKLCH or RGB components, the color is automatically converted back to OKLab (the internal storage format) to maintain consistency.
Copying colors¶
The copy() method creates an independent copy of a Color object. This is useful
when you want to modify a color without affecting the original:
import dartwork_mpl as dm
# Create a color
color = dm.oklab(0.7, 0.1, 0.2)
# Create a copy
new_color = color.copy()
# Modify the copy without affecting the original
new_color.oklab.L += 0.1
new_color.oklab.a = 0.3
print(color.oklab.L) # 0.7 (unchanged)
print(new_color.oklab.L) # 0.8 (modified)
The copied color preserves all color space values and can be modified independently:
import dartwork_mpl as dm
# Create color from any space
color = dm.oklch(0.7, 0.2, 120)
# Copy it
new_color = color.copy()
# Both have the same values in all spaces
L1, C1, h1 = color.oklch
L2, C2, h2 = new_color.oklch
assert L1 == L2 and C1 == C2 and h1 == h2
# Modify independently
color.oklch.C += 0.1
new_color.oklch.h += 30
# Now they differ
assert color.oklch.C != new_color.oklch.C
assert color.oklch.h != new_color.oklch.h
Color space overview¶
OKLab: A perceptually uniform color space where equal distances correspond to equal perceived color differences. Ideal for color operations like blending and interpolation.
OKLCH: OKLab in polar coordinates (Lightness, Chroma, Hue). The cylindrical representation makes it easy to adjust saturation (chroma) and hue independently while maintaining perceptual uniformity.
RGB: The standard red-green-blue color space used by displays and most graphics software. Values are in the 0-1 range.
Hex: Web-standard color representation as hexadecimal strings (e.g.,
#ff5733).
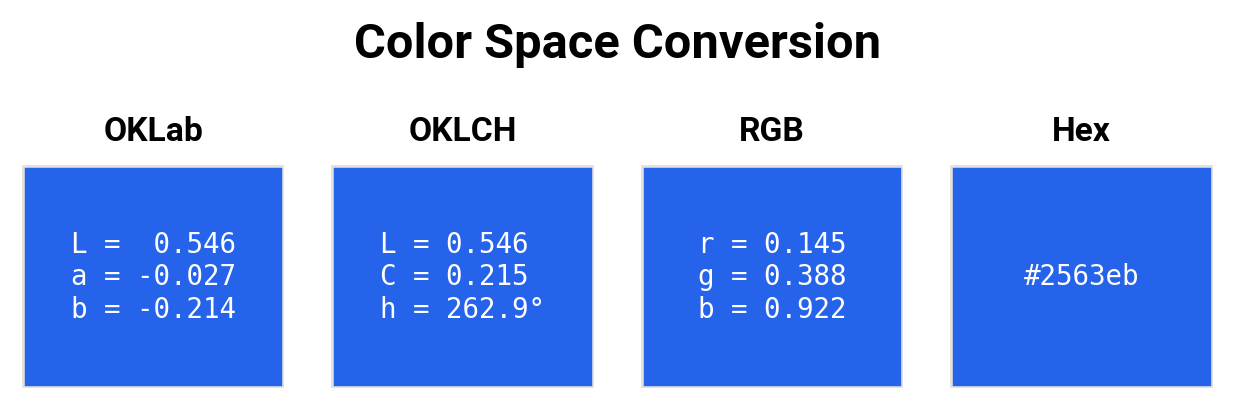
Color space conversion. A single color represented in different color spaces, showing how the same color can be expressed in multiple ways.¶
Color interpolation with cspace¶
The cspace() function generates smooth color gradients by interpolating between
two colors in a specified color space. This is inspired by np.linspace but for
colors.
import dartwork_mpl as dm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
dm.style.use("scientific")
# Interpolate in OKLCH (default, perceptually uniform)
colors_oklch = dm.cspace("#ff5733", "#33ff57", n=10, space="oklch")
# Interpolate in OKLab (perceptually uniform)
colors_oklab = dm.cspace("#ff5733", "#33ff57", n=10, space="oklab")
# Interpolate in RGB
colors_rgb = dm.cspace("#ff5733", "#33ff57", n=10, space="rgb")
Perceptually uniform spaces: Both OKLCH and OKLab are perceptually uniform color spaces, meaning equal distances in these spaces correspond to equal perceived color differences. This makes them ideal for color interpolation, producing smooth gradients where each step appears equally different to the human eye. OKLCH (the default) is particularly convenient because its polar coordinate system makes it easy to adjust saturation and hue independently.
RGB interpolation, in contrast, can produce muddy or uneven transitions, especially in certain color ranges, because RGB is not perceptually uniform.
The function accepts Color objects or hex strings as input:
import dartwork_mpl as dm
start = dm.named("oc.blue5")
end = dm.hex("#ff5733")
gradient = dm.cspace(start, end, n=20, space="oklch")
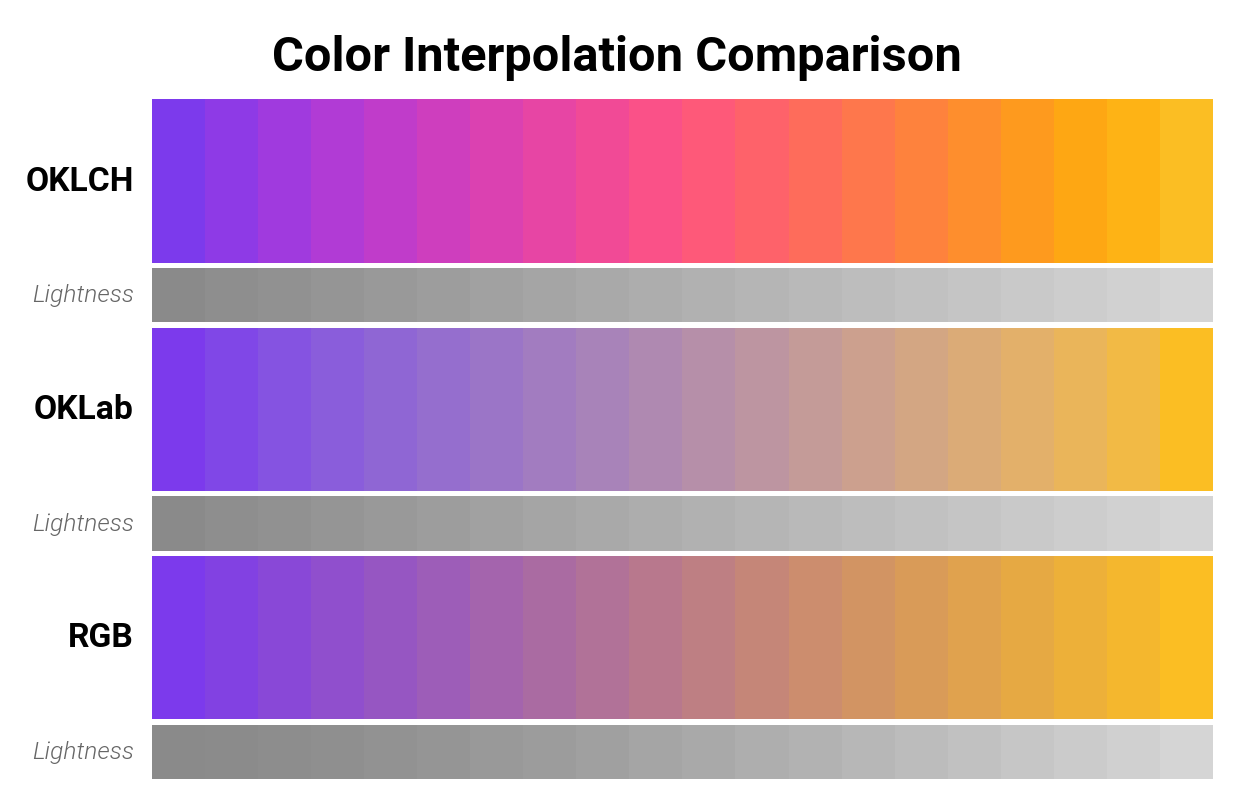
Color interpolation comparison. The same two colors interpolated in OKLCH, OKLab, and RGB spaces. OKLCH produces the most perceptually uniform gradient.¶
Creating custom colormaps¶
You can use cspace() to generate custom colormaps for matplotlib. This is
especially useful for creating perceptually uniform sequential or diverging
colormaps.
import dartwork_mpl as dm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
import numpy as np
dm.style.use("scientific")
# Create a custom sequential colormap
colors = dm.cspace("#1a237e", "#ff6f00", n=256, space="oklch")
cmap = mcolors.ListedColormap([c.to_rgb() for c in colors], name="custom_blue_orange")
# Use it in a plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(dm.cm2in(10), dm.cm2in(6)), dpi=300)
data = np.random.randn(100, 100)
im = ax.imshow(data, cmap=cmap)
plt.colorbar(im, ax=ax, label="Value")
dm.simple_layout(fig)
Diverging colormaps¶
For diverging colormaps, interpolate from one color through a neutral midpoint to another color:
import dartwork_mpl as dm
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
# Diverging: blue -> white -> red
colors1 = dm.cspace("#1a237e", "#ffffff", n=128, space="oklch")
colors2 = dm.cspace("#ffffff", "#c62828", n=128, space="oklch")
colors = colors1[:-1] + colors2 # Remove duplicate white
cmap_div = mcolors.ListedColormap([c.to_rgb() for c in colors], name="custom_diverging")
Registering colormaps¶
To make your custom colormap available throughout your session:
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.colormaps.register(cmap=cmap)
# Now you can use it: plt.imshow(data, cmap="custom_blue_orange")
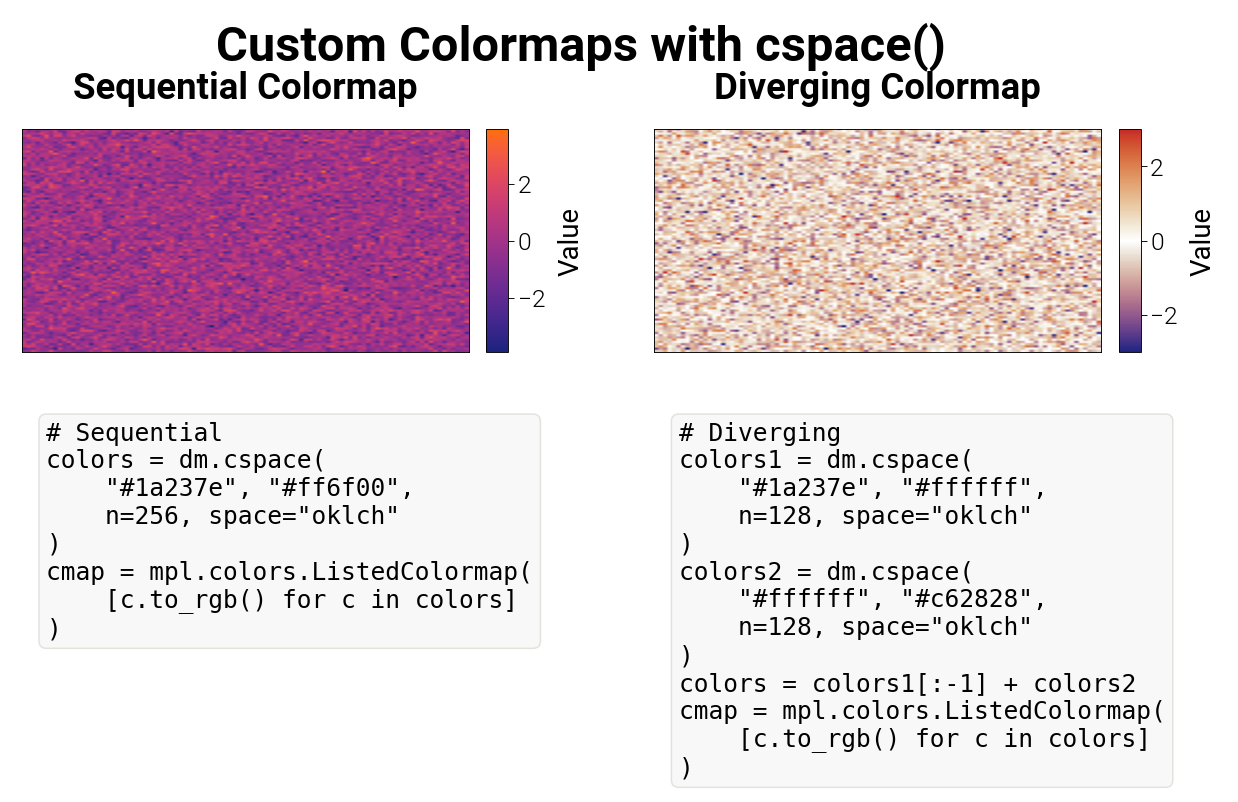
Custom colormaps. Examples of sequential and diverging colormaps created using
cspace() with OKLCH interpolation, applied to sample data.¶
Quick reference¶
import dartwork_mpl as dm
# Create Color objects
color1 = dm.oklab(L, a, b)
color2 = dm.oklch(L, C, h) # h in degrees
color3 = dm.rgb(r, g, b) # auto-detects range
color4 = dm.hex("#ff5733")
color5 = dm.named("oc.blue5")
# Convert between spaces (method-based)
L, a, b = color.to_oklab()
L, C, h = color.to_oklch() # h in degrees
r, g, b = color.to_rgb() # 0-1 range
hex_str = color.to_hex()
# Access color components (view-based, recommended)
L = color.oklab.L # Attribute access
a = color.oklab.a
L, a, b = color.oklab # Unpacking
a = color.oklab[1] # Index access
# Modify color components
color.oklab.L += 0.1 # Arithmetic operations
color.oklab.a = 0.2 # Direct assignment
color.oklch.C *= 1.2 # Modify chroma
color.rgb.r = 0.9 # Modify RGB
# Copy colors
new_color = color.copy() # Create independent copy
# Interpolate colors
gradient = dm.cspace(start, end, n=10, space="oklch") # default
gradient = dm.cspace(start, end, n=10, space="oklab")
gradient = dm.cspace(start, end, n=10, space="rgb")
See also¶
Colors for named color palettes
Colormaps for predefined colormap collections
Usage Guide for general dartwork-mpl patterns